The ________ Reviews and Approves Plans for Systems in All Divisions
Approval processes can benefit organizations of whatever blazon or size, across all industries. You can create an blessing process for whatsoever repeatable arrangement that can exist broken down into discrete steps to formally approve a submitted work. Some of the virtually mutual types of blessing processes include invoice submissions, documents and artistic assets, purchase orders, projected budgets, project plans, college applications and admission, or Nutrient and Drug Assistants (FDA) drug approval.
Below nosotros show you the essential aspects of each of these approval processes, and how to design the process itself. While the specific steps you take to build an approval process will vary based on the system you choose to build it in, these logic maps will aid you define the workflow that works best for the situation and your specific requirements.
How to Create a Content or Certificate Approval Procedure
Content approvals are ubiquitous across all industries and types of organizations. They include whatever creative asset, written piece of work such as an article or social media copy, or whatsoever other documentation that needs approval prior to publication.
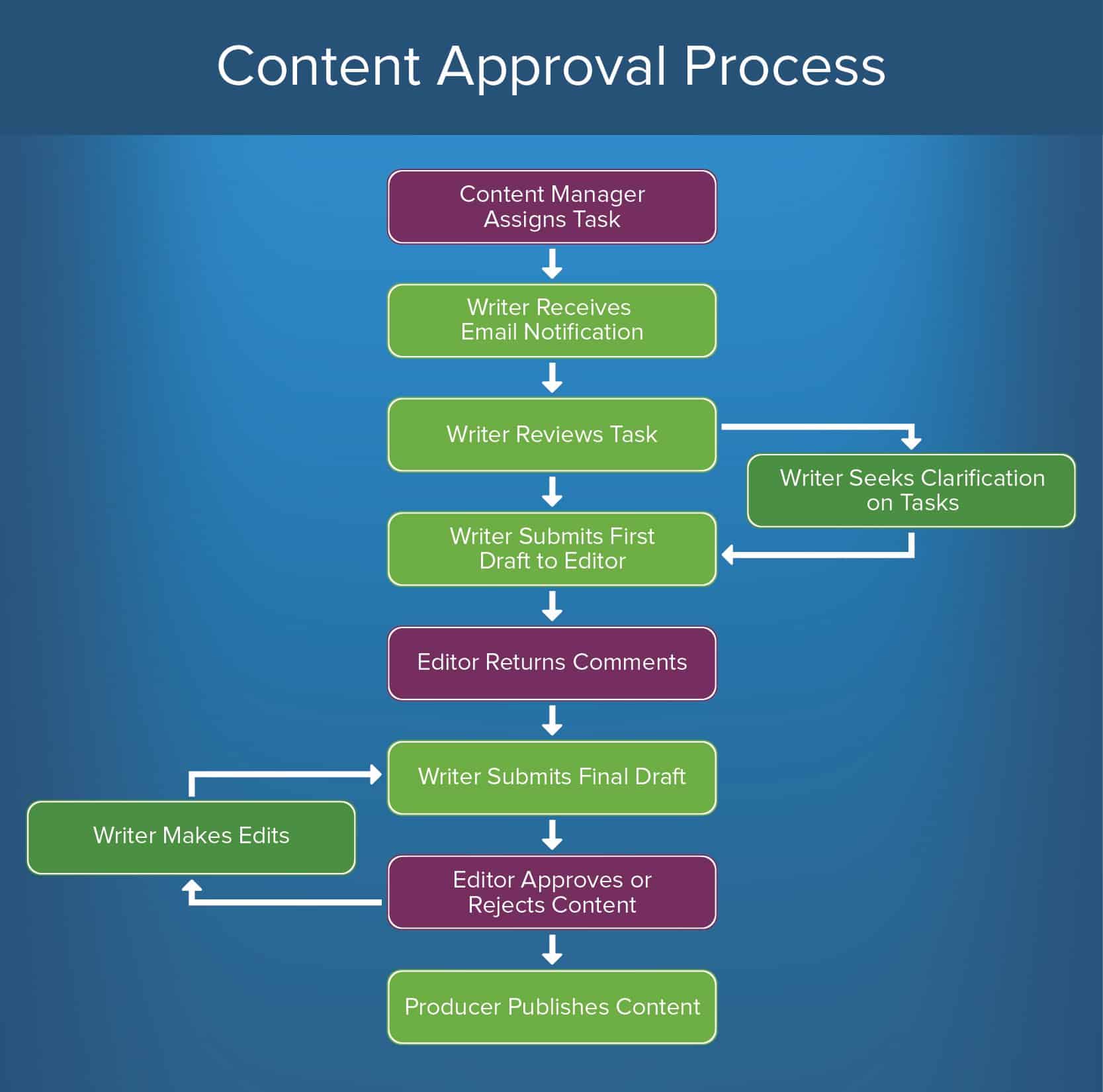
To create a content approval procedure, follow this outline of steps:
- Content Manager Assigns Tasks: The editor creates a schedule of tasks and assigns specific work items to each content producer (in this example, a writer).
- Writer Receives E-mail Notification: Institute a standardized manner to notify writers of their tasks. Email notifications are easy to use and provide a record of assignment.
- Writer Reviews Tasks: The writer reviews the assignment and, if necessary, seeks clarification on tasks from the editor.
- Writer Submits First Typhoon to Editor: This is the initial submission step where the writer submits the outset draft of their work for editor reviews.
- Editor Returns Comments: In most content approval processes, at that place will exist at to the lowest degree one round of edits. So, build in a stride where the editor makes edits and returns the submission to the writer to make additional changes if needed.
- Writer Submits Terminal Typhoon: Once the the necessary edits are made, they return the content to the editor for a second review.
- Editor Approves or Rejects Content: Here the editor has the pick to either approve or reject the content.
- Approve: The content is formally approved.
- Pass up: The writer must brand more edits. This cycle of edits can proceed until the editor is satisfied and the content is officially canonical.
- Producer Publishes Content: Once all edits are finalized, the content is published.
How to Create an Invoice Blessing Procedure
Invoice submission is another common practice that a standardized blessing process can amend. On a monthly ground, you might receive invoices from vendors, contractors, or even internal employees seeking reimbursement, so creating a repeatable, reliable approval procedure will help ensure that everyone is correctly paid on fourth dimension.
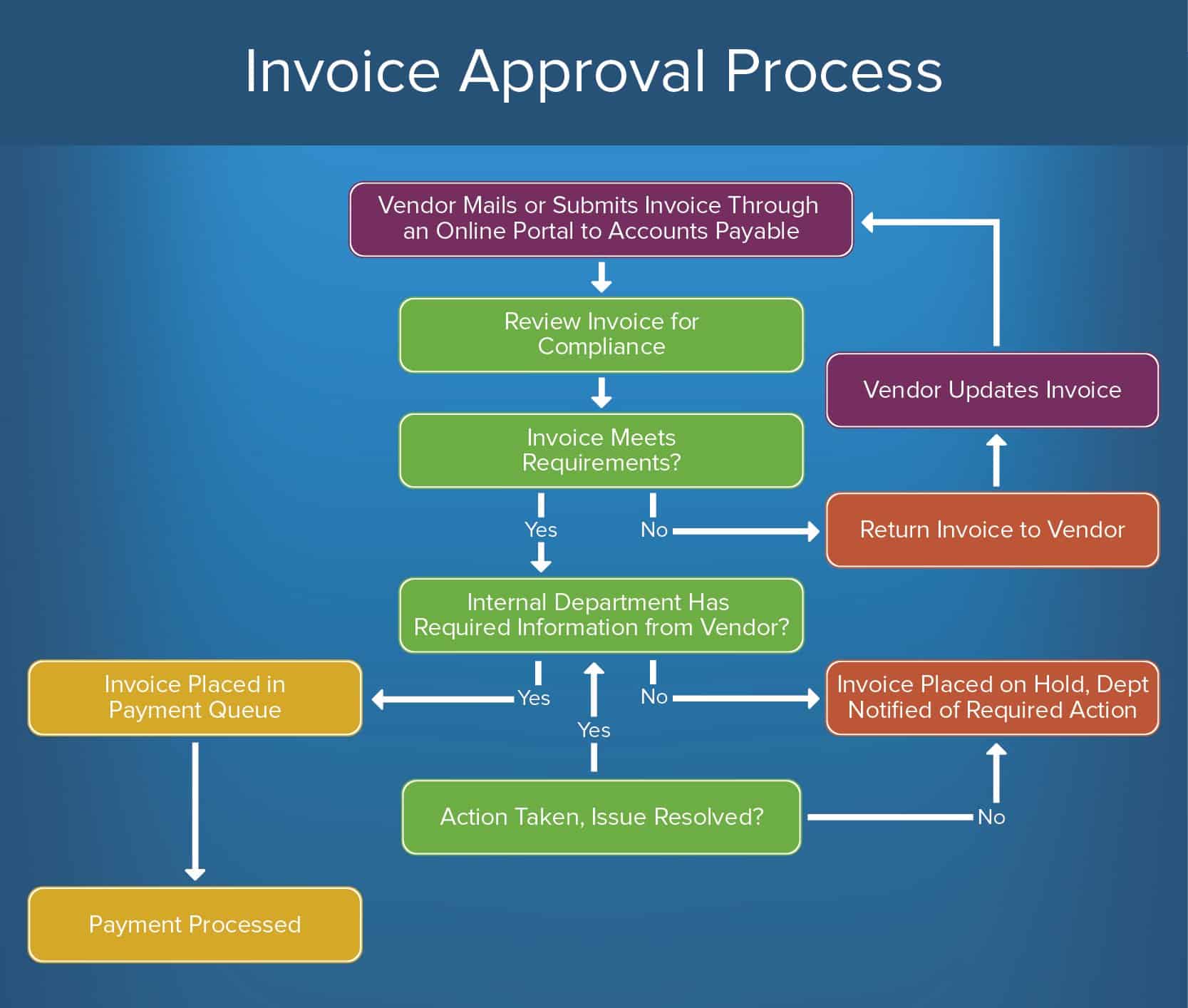
To create an invoice approval process, follow this outline of steps:
- Vendor Mails or Submits Invoice Through an Online Portal to Accounts Payable: The vendor submits their invoice to the correct department or unmarried approver (typically accounting or accounts payable). If using an online portal, the invoice is automatically routed to the correct person or department.
- Review Invoice for Compliance: This is the initial review fabricated by the approving body. Compliance volition differ based on the specific organization, merely in general, the invoice should exist checked for accuracy and include any necessary support documentation. There are two options here:
- Invoice Meets Requirements: The invoice tin move on to the side by side stage in the approving procedure.
- Invoice Does Not Meet Requirements: The invoice is returned to the vendor, who will update and resubmit the invoice.
- Internal Department Has Required Information from Vendor: In social club for an invoice to be processed and payment sent, the approving body often must include supporting information or documentation almost how and why they approved the invoice. Then, build a step into your process to verify that the required back up documentation is included.
- Back up Material Included: The invoice is placed in the payment queue, processed, and sent to the submitter.
- Support Cloth Not Included: The invoice is placed on concur until the approving trunk compiles all necessary documentation. Once this happens, the invoice returns to the concluding review stage and if canonical, is placed in the payment queue and then processed.
How to Create a Purchase Order Approval Procedure
A purchase order (PO) is a document sent from a buyer to a seller to request a certain amount of goods or services at an agreed upon price. Creating an approval process for purchase orders can assistance you monitor the pace of incoming requests, manage inventory and resources, and provide a log of your external business concern.
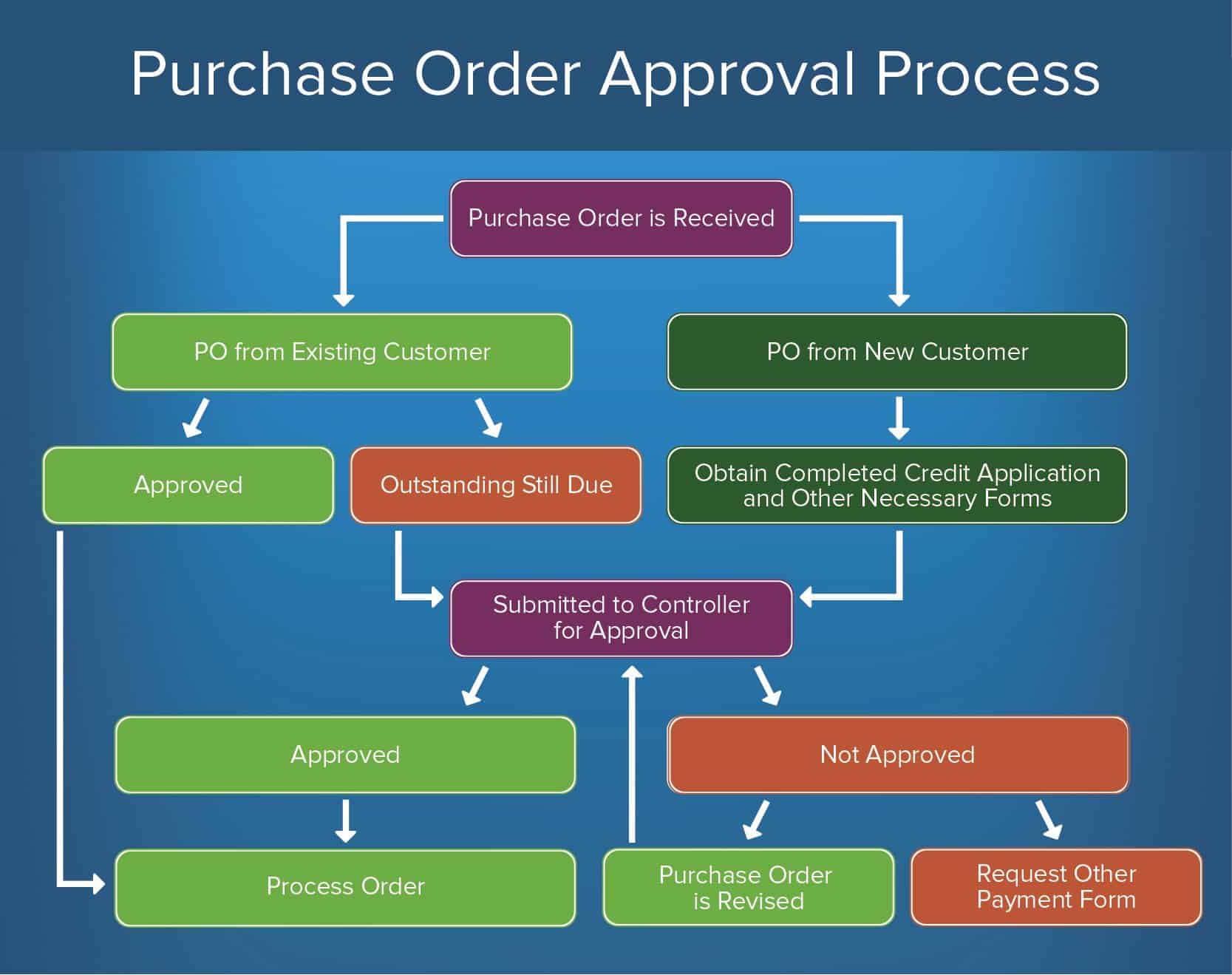
To create a purchase order approval process, follow this outline of steps:
- Purchase Social club Is Received: The buyer formally submits the initial request for appurtenances or services from the seller. Again, consider creating an online submission portal. From here, the road of approval may differ depending on if the PO is from an existing or new customer. Here are both possible scenarios:
- PO from Existing Customer: If the PO is from an existing customer, it is processed one of two means:
- Approved: If everything is right and the customer has no outstanding balance, the PO is approved and the gild is processed.
- Outstanding Notwithstanding Due: If the customer has an outstanding rest, it is sent to another party for review and approval (Step 2 below).
- PO from New Customer: The new customer may take to complete a credit application to ensure that they are equipped to pay for the goods or services requested in the PO.
- PO from Existing Customer: If the PO is from an existing customer, it is processed one of two means:
- Submitted to Controller for Approval: The approval body reviews the PO and any supporting documents (credit application, payment history, etc.) and either approves or rejects the PO.
- Canonical: The purchase order has been approved and the society is candy.
- Non Canonical: The purchase club has failed to meet requirements and is rejected. The heir-apparent will sometimes asking another payment form, or the seller might revise the PO and resubmit it to the controller for approving.
How to Create an Almanac Projected Budget Approval Process
Nigh companies have to propose an almanac or quarterly upkeep earlier they can formally adopt projects and classify funds. Since nearly - if non all - of an arrangement's operations depend on having a pre-canonical budget, it's essential to have an approval process in place.
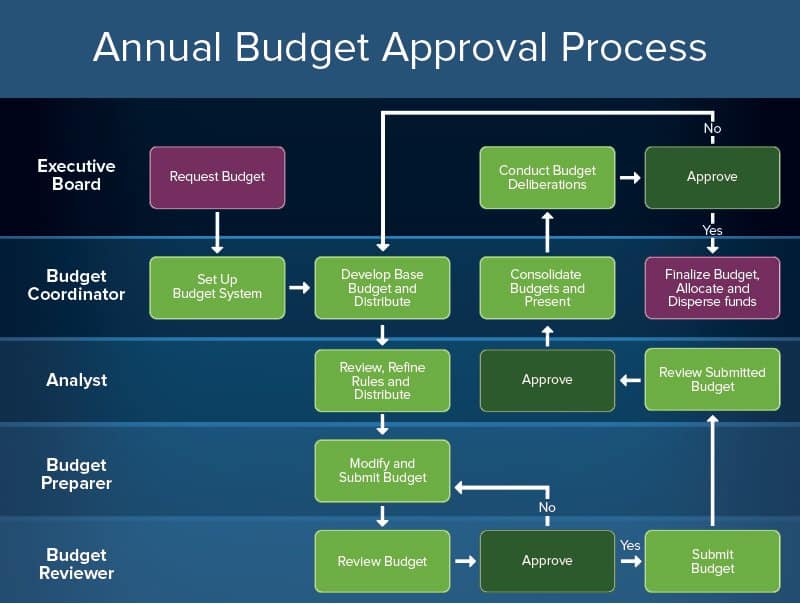
To create a budget approval process, follow these steps:
- Request Upkeep: The executive board submits their proposed upkeep.
- Set Budget System: If yous don't already take a system in place to manage and allocate budget, you lot tin can build this into your approval process. Complete this stride early, as it will inform the rest of your budget review and fund allocation process.
- Develop Base of operations Budget and Distribute: The budget coordinator defines the base almanac budget from which you will measure out the proposed budgetary needs.
- Review, Refine Rules, and Distribute: This is the initial review, commonly performed by an annotator.
- Modify and Submit Upkeep: Internal budget preparers change the proposed upkeep based on the reviewer'south (annotator's) feedback and resubmits it. In some cases, the original submitter (in this case, the executive board) can also be responsible for modifying and resubmitting the budget.
- Review Budget: A designated budget reviewer now reviews the most recent draft of the budget.
- Approved: If approved, the budget reviewer submits the final version of the budget back to the analyst for another circular of reviews.
- Rejected: The budget goes back to the budget preparer for some other round of edits, and is then resubmitted to the upkeep reviewer. This process may require multiple attempts earlier the budget is approved.
- Review Submitted Budget: The annotator performs another review on the submitted budget, which has at present been approved past the budget reviewer.
- Consolidate Budgets and Present: At present that the upkeep has been approved past all analyst and review levels, the budget coordinator compiles the information and presents information technology to the executive lath for concluding sign off.
- Conduct Budget Deliberations: The executive board reviews the changes made by the approving bodies, and either approves or rejects the budget.
- Canonical: The budget is at present officially approved and is adopted into the organization's yearly planning. Funds are allocated.
- Rejected: The executive board resubmits their proposed budget (perhaps with modifications) to the upkeep coordinator; the cycle begins once more at Stride 3.
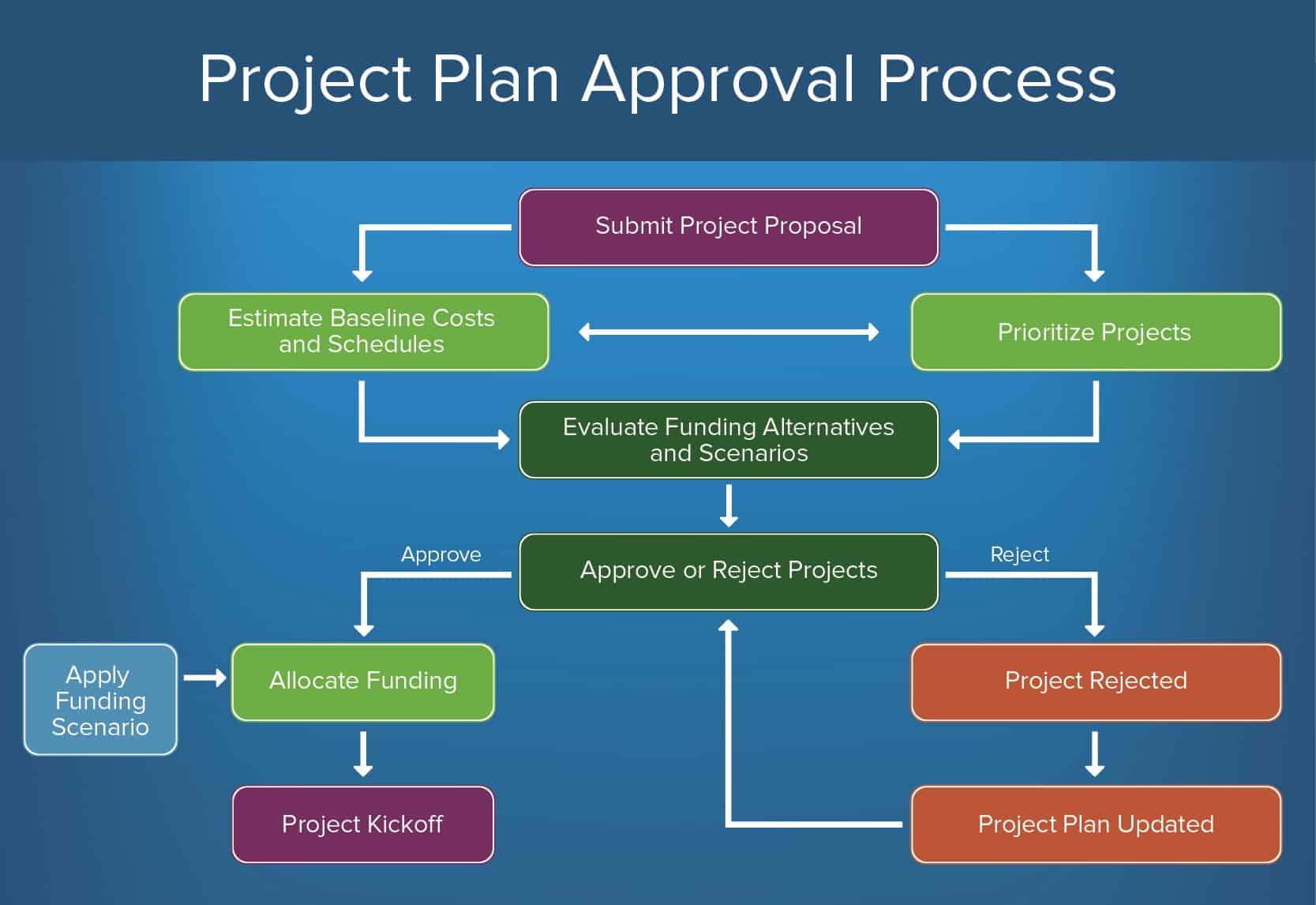
How to Create a Projection Programme and Budget Approval Process
Every project that an organization adopts must first pass through a series of approvals. With so many competing projects, budgets, and departments, an approval process helps organize and prioritize projects.
To create a project programme and budget approval process, follow this outline of steps:
- Submit Project Proposal: This is the initial submission, where teams ascertain and request the project they want to take on. You can find a project plan template here.
- Judge Baseline Costs and Schedules and Prioritize Projects: In these phases, typhoon a upkeep and timeline based on your project proposal, and roughly prioritize projects. In that location may be some back and forth betwixt these two steps before advancing to the side by side step.
- Evaluate Funding Alternatives and Scenarios: It'southward important to consider alternatives - both to your project specifications and upkeep - in the event that your proposal is rejected. Build in a step to draft other options, or aspects of your initial plan.
- Approve or Reject Projects: The proposal is reviewed by the approval body and either approved or rejected.
- Approved: If canonical, funding is allocated for your project and y'all can agree a project kickoff.
- Rejected: If rejected, the proposal is terminated. However, you can also build a step for submitters to revise the project programme and resubmit for blessing.
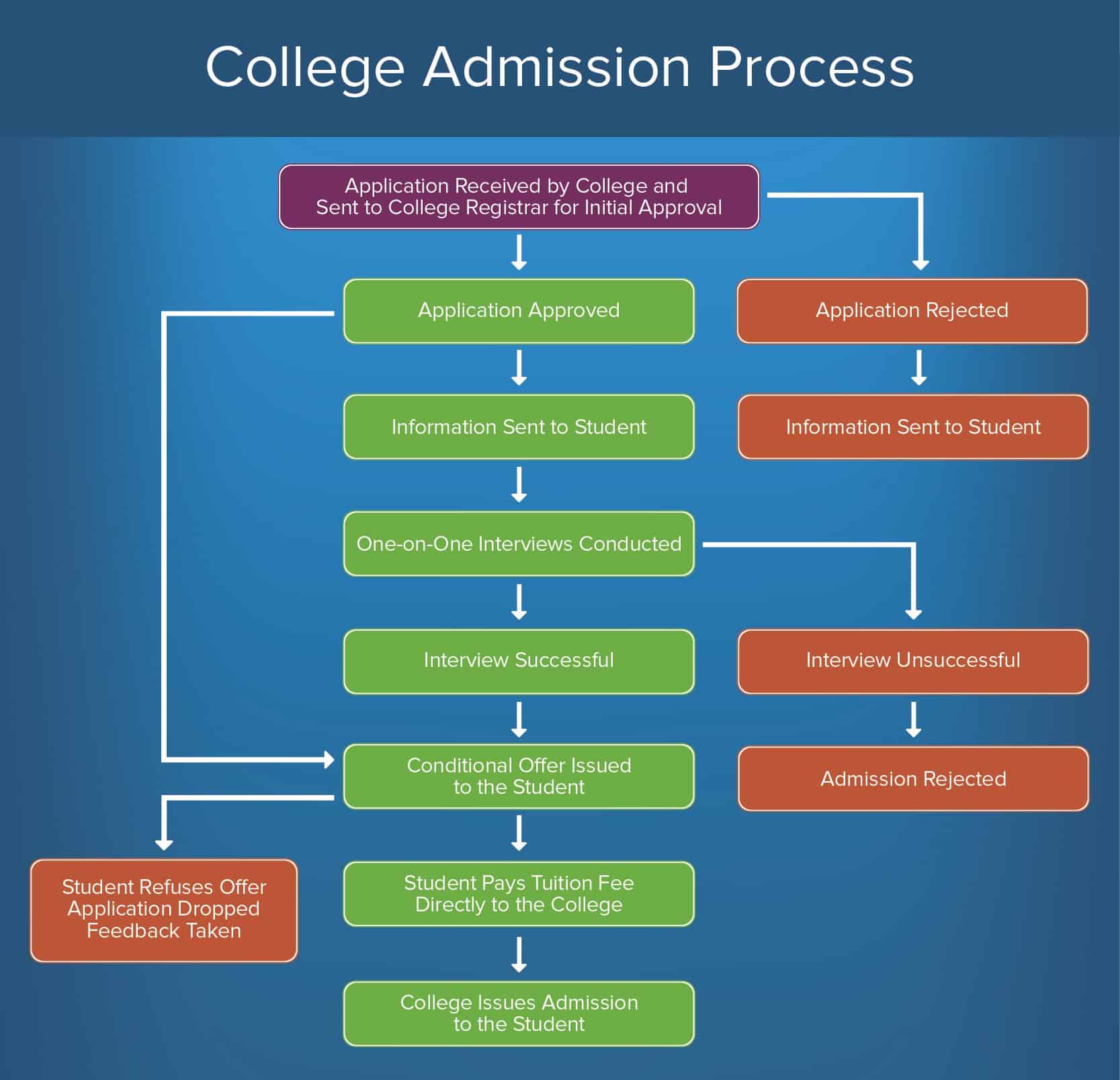
How to Create a College Acceptance and Admission Procedure
Colleges and universities receive a high volume of applicants and equally such, must create an automated, consequent approval process for admitting and enrolling students. While the steps listed below are what academic institutions might follow, yous can likewise edit the procedure outline for admission to other programs.
To create a college acceptance and admission process, follow this outline of steps:
- College Awarding Received and Routed to Higher Registrar for Initial Approving: The application is submitted (typically through a portal such as the Common App or a academy website). The registrar, or any other administrative approving body, performs an initial screening and either approves or rejects the application.
- Approved: The application passes the initial screening and adjacent-step data is sent to the student applying.
- Rejected: The student's application is terminated and information is sent to the bidder.
- Carry I-on-Ane Interviews: Many academic institutions require interviews as office of the application procedure. However, some don't, and so this step is optional.
- Interview Successful: If the interview is successful, the college or university issues a conditional offer to the applicant and moves onto the next stage.
- Interview Unsuccessful: The student's awarding is rejected.
- Conditional Offer Issued to the Student: The university formally offers the applicant admission. The student can have or reject the offer.
- Students Accepts Offer: Educatee accepts the conditions of the university's offer and pays tuition to the school.
- Student Refuses Offer: The application is dropped. At this point, the university might also solicit feedback from the applicant to employ for future awarding cycles.
- College Issues Admission to the Educatee: One time the higher receives the tuition, the student is enrolled in the university.
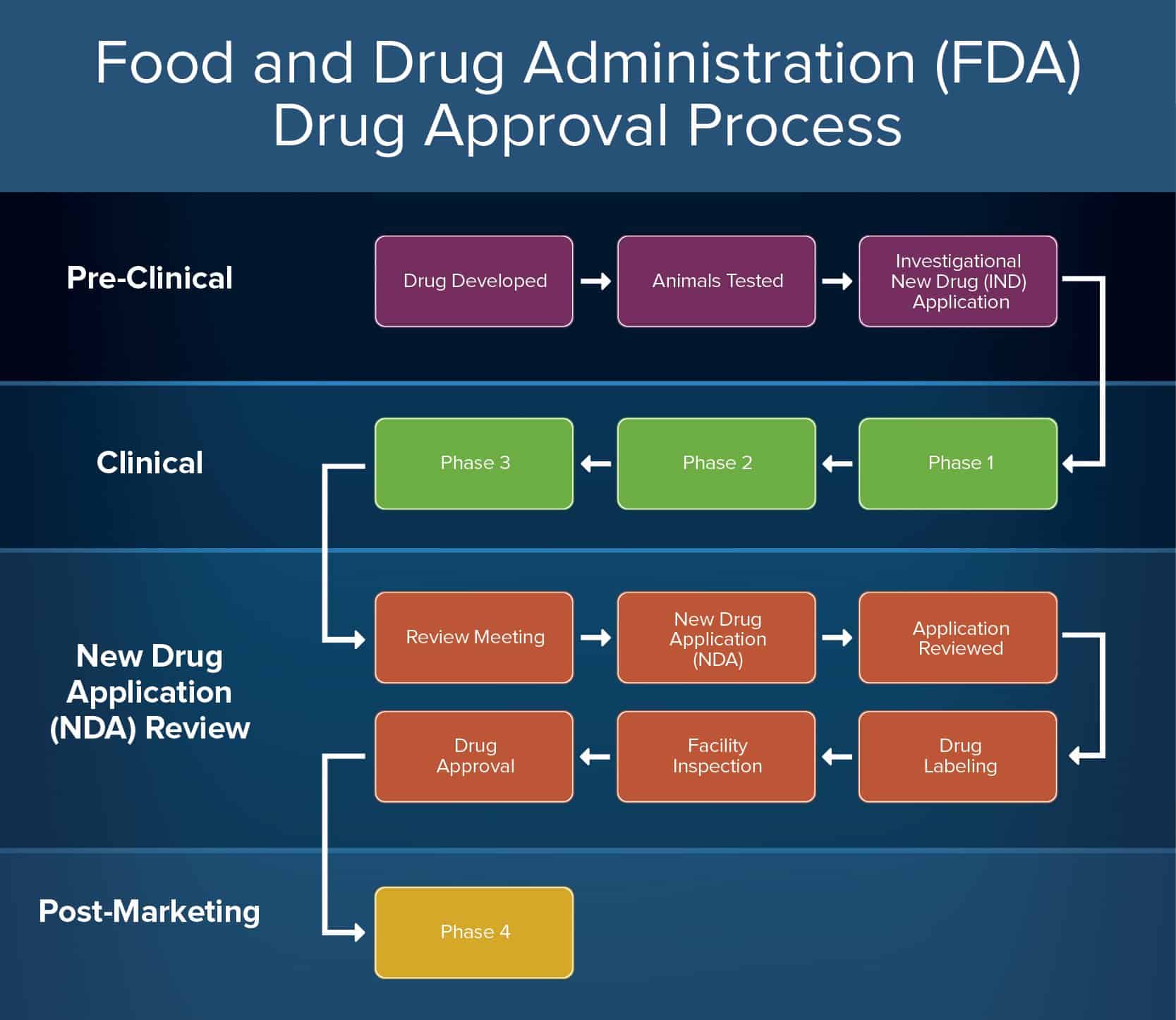
How to Create a Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Drug Approval Process
Every pharmaceutical drug on the market place today in the U.S. has to pass through a lengthy approval process, as enforced past the Nutrient and Drug Administration (FDA). The post-obit outline is taken direct from the FDA'due south website.
Phase One: Pre-Clinical: In this stage, the person or body sponsoring the drug (drug sponsor) discovers and screens the drug.
- Drug Adult and Animals Tested: One time the sponsor has adult a new drug and wants to have it approved past the FDA, they perform creature testing to gain information on the prophylactic and efficacy of the drug chemical compound.
- Investigational New Drug (IND) Application: The drug sponsor submits an IND awarding to the FDA to seek approval. This application includes information on the results of the beast tests, too as on the composition and manufacturing of the drug.
Stage 2: Clinical: This stage consists of the drug sponsor'south clinical studies and trials of the proposed drug.
- Phase 1 (20-80 volunteers): This testing phase is primarily concerned with identifying the most mutual side effects, and how the drug is candy within the human body. Information technology emphasizes rubber.
- Phase 2 (hundreds of volunteers): This phase emphasizes effectiveness, and tests how the drug affects a certain affliction or illness.
- Phase 3 (thousands of volunteers): In this phase, testers gather more information about both the safety and effectiveness of the proposed drug. They besides test it in combination with other drugs, unlike dosages, and different populations to understand the effects.
Phase Iii: New Drug Awarding (NDA) Review: The FDA performs a comprehensive review on the new drug to ensure information technology meets requirements and is safe to approve.
- Review Meeting: The FDA meets with the drug sponsor to discuss the findings of the testing.
- NDA Application: The sponsor submits a formal application, and includes all data from the tests they've completed on both animals and humans.
- Application Review: The FDA has sixty days to review the NDA application and determine whether or non to file information technology.
- Filed: If the FDA files the NDA, it moves on to the next review step.
- Not Filed: The FDA can too cull not to file the NDA. At this point, the drug proposal is terminated.
- Application Reviewed: If the FDA decides to file the NDA, they perform a review of the awarding to evaluate the sponsor's research and the drug itself.
- Approved: If approved, the drug moves on to the side by side step.
- Rejected: If rejected, the proposal is terminated.
- Drug Labeling: The FDA reviews the official drug labelling and edits it to ensure the proper messaging and advice to health care professionals and consumers.
- Facility Inspection: The FDA performs an inspection of the facilities where the drug volition be manufactured to ensure safety.
- FDA Drug Approval: The drug is formally approved past the FDA.
Stage Four: Post-Marketing: Ongoing efforts by healthcare industries to appropriately market the drug to the public.
Source: https://www.smartsheet.com/approval-process-workflow
0 Response to "The ________ Reviews and Approves Plans for Systems in All Divisions"
Post a Comment